OpenAI, an artificial intelligence (AI) research organization, announced ChatGPT, a dialogue-based prototype chatbot that can understand and reply to natural language. People are now stunned by how intelligent the AI-powered bot sounds. Since it may provide direct solutions to complicated problems, it has even been referred to as a Google replacement by certain users. Chat GPT is getting a lot of attention.
The introduction of a new technology named GPT-3 in 2020 sparked a lot of discussion in the chatbot and artificial intelligence (AI) industries. Based simply on online data, this new machine-learning model was able to produce any kind of writing. And it was the most accurate representation of its kind ever made! The GPT-3 chatbots are so advanced, according to OpenAI, the company that created the technology, that they can pass the Turing test. The Turing test determines whether a machine's behavior is identical to that of a human. The Turing test is named after mathematician Alan Turing.
Though the GPT-3 model appears to be quite a technological advancement, is there any potential for commercial application? Businesses have begun to consider the GPT-3 model's application and how it might benefit their operations. If true, what may its primary applications be? Are there any drawbacks? What are the implications of GPT-3 for AI chatbot development? Is this development really as important as some people say it is, or is it just hype? We will examine the advantages and disadvantages of GPT-3 chatbots as well as their potential for Conversational AI. We will be discussing everything in detail.
What are GPT-3 Chatbots?
GPT-3 chatbots are programmable artificial intelligence applications that use the GPT-3 language model and are based on OpenAI's ongoing development. The trained language processing software that runs these bots, also known as "Generative Pretrained Transformer 3" contains more than 175 billion machine learning parameters. The parameters assist the GPT-3 bot in analyzing communication input (such a request for customer support) and producing the appropriate response.
Companies can train the computer to communicate in written or spoken ways that are human-like when developing GPT-3 chatbots, utilizing a platform like OpenAI's GPT-3 engine. To generate natural dialogue with clients, the advanced program uses deep learning, NLP, operator instructions, a sizable knowledge library generated from an online training data set, and other techniques. Python and Twilio’s SMS are common languages and platforms that use GPT-3 technology.
GPT-3 bot messaging services may respond to a client query in a way that is genuinely helpful, unlike other simpler chatbots. Thanks to its user-friendly application programming interface, training the complicated language model technology is rather straightforward (API). The provider often configures the bot to serve a specific function (such as customer service), while the end-user assists with the fine-tuning necessary for their particular application or business needs.
Companies can enter text into an API teaching tool to train the GPT-3 bot and take into consideration specific "gotchas." Then, the software will work to create a response based on the information. After a few iterations of training, the GPT-3 bot's algorithm will provide future responses based on the presentation's style, tone, and content.The GPT-3 datasets aren't updated in real-time and can be many years old, thus unless they are specially written in, new advancements in a given field, such as specific terms or jargon, might not be able to be incorporated into your workflow.
Advantages
GPT-3 is not commonly used in production. You can see some examples of its use cases in the examples below:
Coding : There are various web demos where individuals show off GPT-3's ability to convert instructions from human language into code. Please be aware, though, that none of these are reliable systems that are ready for production. They are founded on online examples of GPT-3's effectiveness: Python GPT-3 has been able to code basic tasks in Python. SQL GPT-3 can automatically generate SQL statements from simple text descriptions without the assistance of human operators.
Machine Learning/Deep Learning Frameworks : GPT-3 has been used to build code for machine learning and deep learning frameworks like Keras.
DevOps Services : It has been used to create, delete or list DevOps services on the cloud. If it could work in a robust, predictable way, it would be able to automate the management of these services.
Front End Design : Using CSS or JSX, it may create website layouts that meet user requirements.
Chatbots : Numerous GPT-3 chatbots have been created because GPT-3 can carry on conversations that resemble those with humans. It has the ability to advance today's chatbots even though there are still significant areas for improvement. It can translate, respond to general inquiries, and serve as a search engine with precise responses and source connections without the requirement for case-specific pre-training.
Auto-Completion : GPT-3 was built for auto completion and is the most human-like system for that as explained by the IDEO team who used it as a brainstorming partner.
Few more examples of GPT-3's effectiveness -
- Chat GPT can fix your Code
- Chat GPT can do your homework
- Chat GPT can generate prompts.
- Chat GPT can build your website.
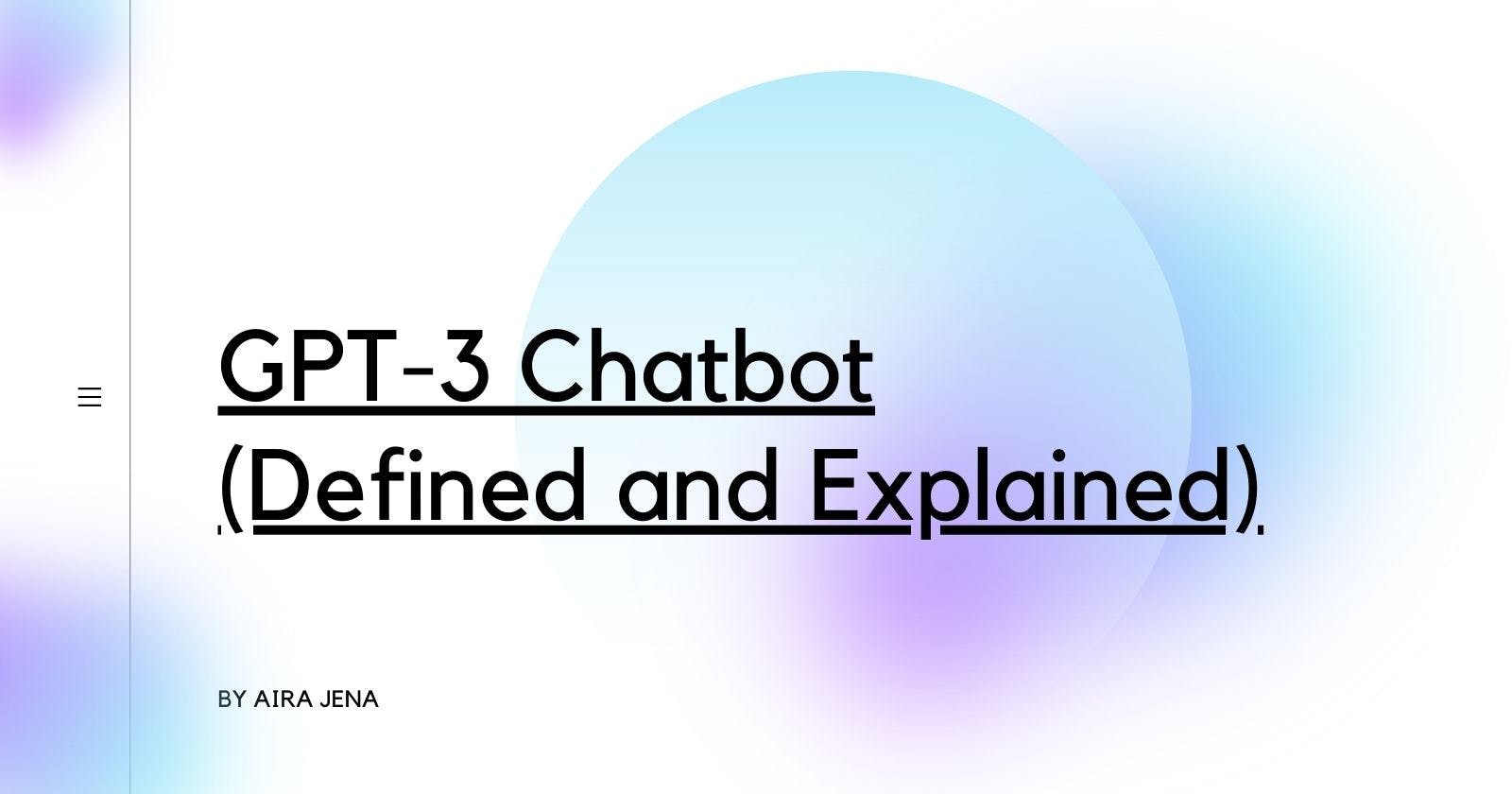
Google vs Chat GPT Response.
Limitations
ChatGPT occasionally provides responses that are valid yet inaccurate or illogical. Fixing this problem is difficult because: (1) There is currently no source of truth during RL training; (2) Making the model more cautious makes it decline questions that it can answer correctly; and (3) Supervised training causes the model to be misled because the ideal response depends on the model's knowledge rather than the demonstrator's knowledge.
The input phrase can be changed, and ChatGPT is sensitive to repeated attempts at the same question. For instance, the model might claim to not know the answer if the question is phrased one way, but with a simple rewording, they might be able to respond accurately.
The model frequently overuses particular words and phrases, including repeating that it is a language model trained by OpenAI. These problems are caused by over-optimization problems and biases in the training data (trainers prefer lengthier replies that appear more thorough).
When the user provides an uncertain query, the model should ideally ask clarifying questions. Instead, their present models typically make assumptions about what the user meant.
Although they have made an effort to have the model reject unsuitable requests, occasionally it will follow harmful instructions or behave biasedly. Although they anticipate some false negatives and positives for the time being, they are using the Moderation API to alert users to or prohibit specific categories of harmful content.
GPT-3 technology will improve with training
The GPT-3's erratic responses are a contributing factor in the industry's reluctance, but this can be reduced with minor changes. Giving the GPT-3 more instances of anticipated responses is one method to improve the output quality, according to Godin. The AI expert also suggested that adding detection mechanisms to GPT-3 and teaching it about inappropriate topics could help prevent it from providing improper replies. To sum up, this versatile and hence strong instrument nevertheless need instruction, training, and time to develop fully.
The potential of GPT-3 and conversational AI
Despite its drawbacks, GPT-3 may eventually be applied to enhance conversational AI chatbots. GPT-3s could train NLP chatbots with expressions using their conversational abilities and the massive amounts of data they have access to. This would free up the work of conversation designers and raise the standard of NLP bots. As previously indicated, another potential application for GPT-3s would be the development of a brand-new search engine that, in the future, might even compete with Google or Bing. It will be interesting to see how AI chatbots develop as they combine with a tool with a wealth of data like GPT-3 as they get more advanced.
GPT-3 Chatbots for Customer Service
The flexible language model and user-friendly API of GPT-3 technology have the potential to revolutionize AI-powered customer support, despite the fact that it has not yet attained the same level of mainstream adoption as the regular chatbot that is frequently seen on websites, smartphones, and computers. GPT-3 bots are able to assess, comprehend, and answer to consumer inquiries. They can also predict demands based on a single phrase and improve the human-likeness of their responses over time. And things are only getting better over time. Companies can enhance customer assistance while cutting expenses by utilizing the advanced power of GPT-3. GPT-3 chatbots are capable of producing conversations that are nearly impossible to distinguish from those of actual customer support representatives (though sometimes it can output some hilarious or scary content). In the best situations, this AI system can handle support inquiries without the assistance of a live customer service representative or any other factors.
Improved Communication : Deep learning is used by GPT-3 chatbots to process approximately 500 billion words and numbers. The responses from the bots can then be customised by businesses utilising GPT-3's simplified API. The language model can leverage predictive technology to predict client demands, assess and reply to consumer inquiries, and give self-service resources that are appropriate for the conversation's context. Additionally, users of GPT-3-powered instant messaging applications can connect instantaneously with "someone," which decreases lag time and, in theory, increases user satisfaction. Before escalating issues to live agents, the bots can also gather relevant information. This enables customer care representatives to give priority to certain inquiries and lowers support expenses by at least 30%.
Enhanced Support for Customer Service Agents (the preferred option) : GPT-3 chatbots that can be programmed can assist in providing information to customers and guiding them to useful resources. However, even the greatest chatbots cannot completely eliminate the need for real operators in the majority of companies' customer support departments. By clarifying customer requests, escalating issues to the appropriate channel, querying CRM libraries and product listing databases and presenting relevant solutions for the customer service agent to relay, and storing previous interactions to ensure personalised assistance, GPT-3 bots can support customer service departments.
Increased Customer Satisfaction : In an Uberall poll, 80% of respondents said they had a pleasant experience using AI-powered bots. To improve customer happiness, the technology operates on numerous levels. The increasingly common virtual technology is starting to play a vital role in some areas for Internet-based customer service departments around the world, from rapid responses to more effective solutions.
How Do GPT-3 Chatbots Work?
Using GPT-3 technology to improve automated instant messaging systems gives users the ability to analyze and comprehend client inquiries and have human-like conversations. Scripted bots receive an immediate boost from GPT-3's contextual comprehension and pattern recognition. As a result, bots may quickly detect a change in the context of a discussion and access new data to provide a response. The name of the software package, Generative Pretrained Transformer, describes the operations that drive the GPT-3 language model. In order to anticipate or create an output based on a particular digital input, such as a user's query, generative language models use statistics. Customer service departments can easily implement the pre-trained technology without the need for their own AI and ML resources. The application's transformational features may locate a keyword within a phrase, ascertain how frequently the words appear together, and then utilize the prediction to produce a suitable, human-like response. The ability of GPT-3 technology to extract context and meaning from both structured and unstructured interactions is perhaps its most significant feature. In turn, it can build knowledge graphs that enhance chatbot responses and then broaden those knowledge graphs.
Method of GPT-3 Chatbots
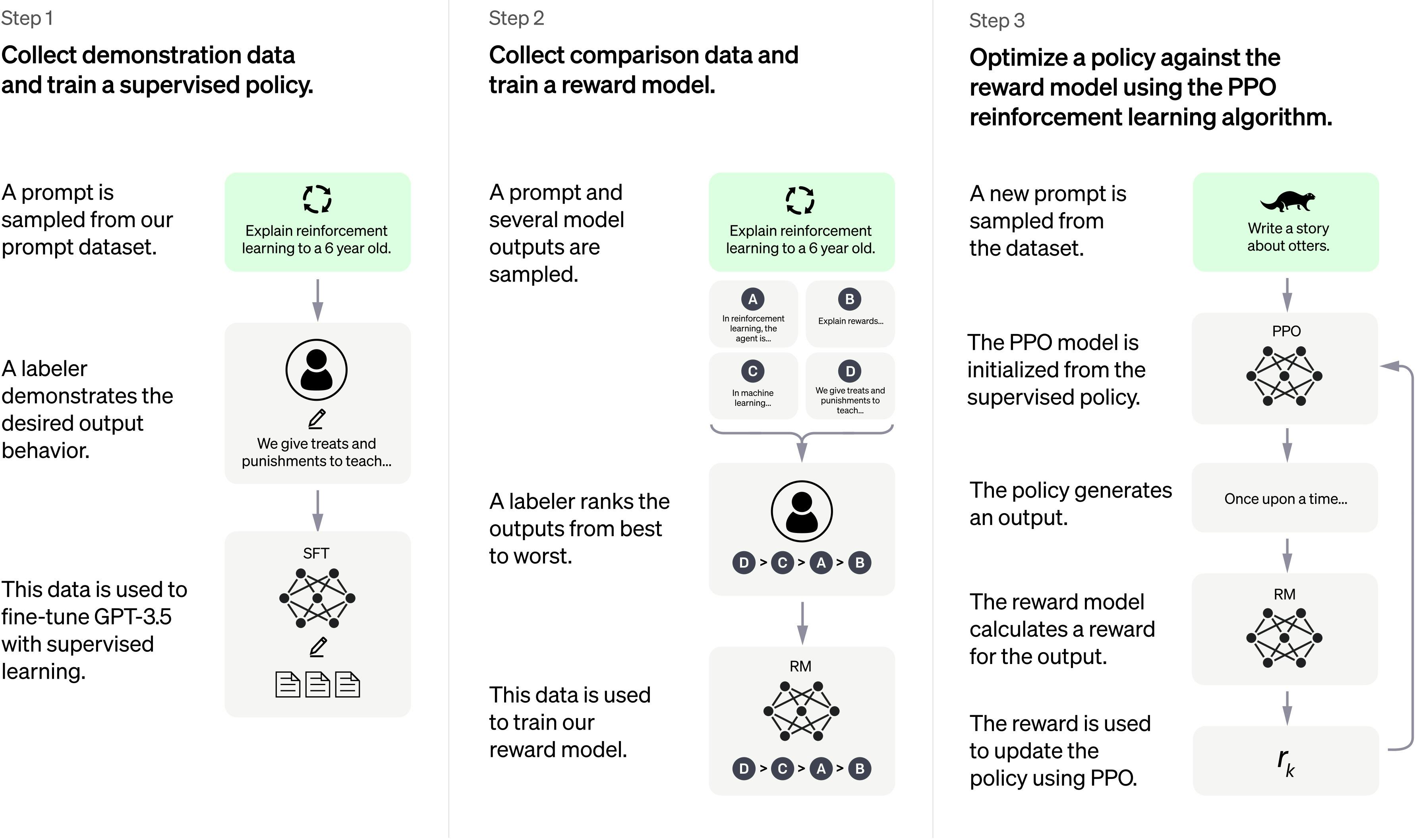
Similar to InstructGPT, they used Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) to train this model, with a few minor variations in the data collection arrangement. They used supervised fine-tuning to train an initial model by having human AI trainers act as both the user and the AI assistant in chats. They provided the trainers with access to sample writing recommendations to assist them in creating their responses. They needed comparison data, which included at least two model replies ordered by quality, in order to build a reward model for reinforcement learning. They used the chatbot interactions that AI trainers conducted with it to get this data. Researchers chose a model-written statement at random, sampled a number of potential conclusions, and asked AI trainers to rank them. They can use Proximal Policy Optimization to adjust the model using these reward models. This method was iterated upon multiple times. The model used to train ChatGPT, which ended training in early 2022, is from the GPT-3.5 series. The 3.5 series is covered in more detail here. On a supercomputing infrastructure powered by Azure AI, ChatGPT and GPT 3.5 were trained.
Conclusion:
There still exists difficulty when we try to make complex AI systems to behave exactly as we want them to (also known as the AI alignment problem), and according to some researchers, we'll encounter many issues when we give more advanced AI models more control. Overall, ChatGPT is unquestionably a tremendous advance over past systems, but these models still have some serious issues that require further research. Finding flaws in such public demos is exactly what OpenAI (and many others in the AI field) contend. When will businesses start introducing these systems into the public is the question. And when they do, what will happen?